Wheatstone Bridge
Wheatstone Bridge: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Wheatstone Bridge, Balanced Wheatstone Bridge & Unbalanced Wheatstone Bridge etc.
Important Questions on Wheatstone Bridge
Figure shows an unbalanced Wheatstone bridge. What is the direction of conventional current between and ?
If the central resistance is , then the equivalent resistance between and will be
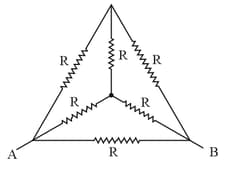
Find the equivalent resistance between and .
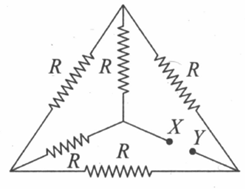
The effective resistance between and is
As shown in the figure below, a cube is formed with ten identical resistance (thick lines) and two shorting wires (dotted lines) along the arms and .
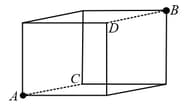
The resistance between points and is
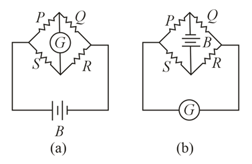
Figure below shows a Wheatstone bridge in which are fixed resistances, is a galvanometer and is a battery. For this particular case, the galvanometer shows zero deflection. Now, only the positions of and are interchanged, as shown in figure . The new deflection of the galvanometer-
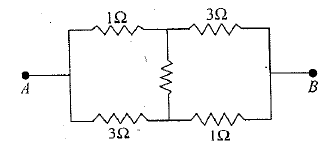
Find the equivalent resistance between and .
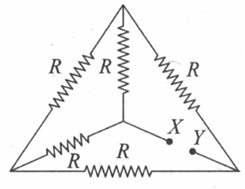
The effective resistance between points P and Q of the electrical circuit as shown in the figure is
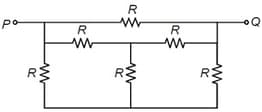
What is the value of in Ohms such that the current in the galvanometer is zero?
In the arrangement of resistances shown below, the effective resistance between points and is
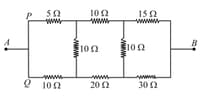
Find the equivalent resistance between the points and
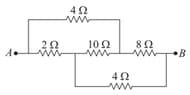
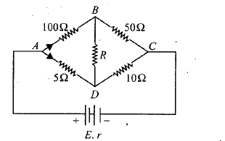
In a Wheatstone bridge the branch resistances are as shown in the following circuit diagram. What will be the value of in balancing the condition of the Wheatstone bridge?
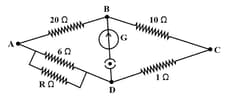
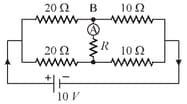
What will be the value of resistance for the network shown in the figure so that the current in ammeter may be zero.
On interchanging the position of battery and galvanometer in Wheatstone bridge respectively the new balance point:
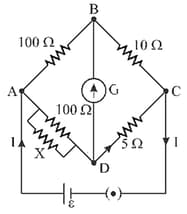
In the circuit shown in figure, the cell is ideal with emf . If the resistance of the coil of galvanometer is , then
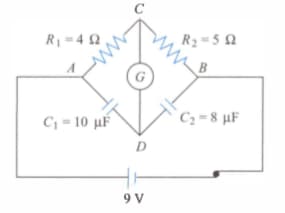
Resistance and are arranged in a cyclic order to form a balanced Wheatstone’s network. The ratio of power consumed in the branches and is:
In a Wheatstone network, and . The resistance with which is to be shunted in order that the bridge may be balanced is
In the adjoining circuit, the resistances are given in ohm, and are unknown resistances. The current through the resistance is while that through the resistance is No current passes through the galvanometer. The values of the unknown resistances and are respectively

In a Wheatstone bridge (see figure), resistances and are remain unchanged. When the bridge is balanced. On interchanging and , the value of for balanced bridge is . The value of is close to:
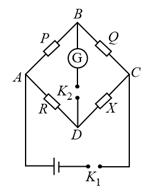
In a Wheatstone bridge setup, and are approximately equal. Initially at balancing conditions. When and are inter changed, then bridge is balanced for . Then the value of is.